procs #
procs is a replacement for ps written in
Rust.

Documentation quick links #
Features #
- Colored and human-readable output
- Automatic theme detection based on terminal background
- Multi-column keyword search
- Some additional information which are not supported by
ps- TCP/UDP port
- Read/Write throughput
- Docker container name
- More memory information
- Pager support
- Watch mode (like
top) - Tree view
Platform #
- Linux is supported.
- macOS is experimentally supported.
- macOS version is checked on Travis CI environment only.
- The issues caused by real-machine are welcome.
- Windows is supported.
Installation #
Download binary #
Download from release page, and extract to the directory in PATH.
 #
#
Nixpkgs #
You can install from Nixpkgs.
nix-env --install procs
snapcraft #
You can install from snapcraft.
sudo snap install procs
homebrew #
You can install from homebrew.
brew install procs
MacPorts #
You can install from MacPorts.
sudo port install procs
Alpine Linux #
You can install from the Alpine Linux repository.
The correct repository (see above link for the most up-to-date information) should be enabled before apk add.
sudo apk add procs
Arch Linux #
You can install from the Arch Linux community repository.
sudo pacman -S procs
Scoop #
You can install with scoop.
scoop install procs
Fedora #
sudo dnf install procs
RPM #
You can install with rpm.
sudo rpm -i https://github.com/dalance/procs/releases/download/v0.14.0/procs-0.14.0-1.x86_64.rpm
Cargo #
You can install with cargo.
cargo install procs
Installation Notes #
Permissions issues #
On macOS, normal users can’t access any information on other users’ processes. On Linux, normal users can’t access some information (ex. Read/Write throughput) of other users.
If you want to show this information, you should use sudo.
$ sudo procs
[sudo] password for ...:
If you want to skip password input, you can add the following entry to /etc/sudoers.
[user or group] ALL= NOPASSWD: [procs binary path]
// ex. myuser ALL= NOPASSWD: /usr/local/bin/procs
Usage #
In the following screenshots, config/large.toml is used as the configuration.
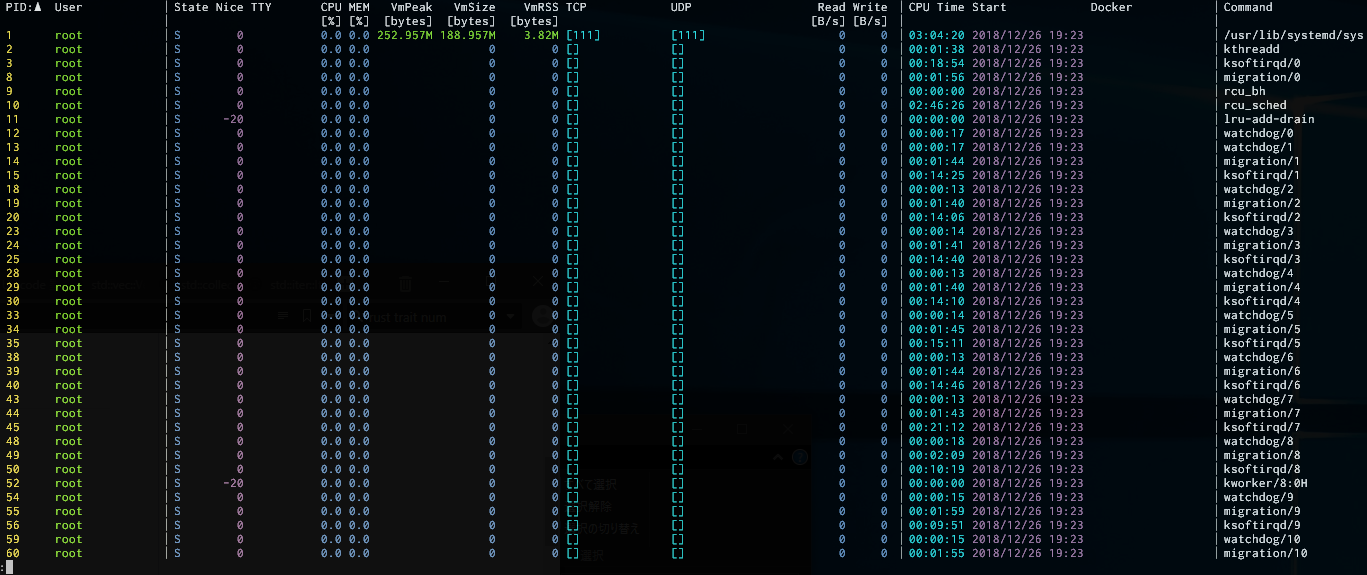
Show all processes #
Type procs only. It shows the information of all processes.
procs
Search by non-numeric keyword #
If you add any keyword as argument, it is matched to USER, Command by default.
procs zsh
If you want to add columns matching to non-numeric keyword, nonnumeric_search option can be used in configuration file.

Search by numeric keyword #
If a numeric is used as the keyword, it is matched to PID by default.
Numeric is treated as exact match, and non-numeric is treated as partial match by default.
procs --or 6000 60000 60001 16723
If you want to add columns matching to numeric keyword, numeric_search option can be used in configuration file.

Note that procfs permissions only allow identifying listening ports for processes owned by the current user, so not all ports will show up unless run as root.
Logical operation of search keywords #
If there are some keywords, logical operation between the keywords can be specified by commandline option.
--and: The processes that match with all keywords are shown.--or: The processes that match with any keyword are shown.--nand: The processes are shown unless these match with all keywords.--nor: The processes are shown unless these match with any keyword.
The default operation can be specified in the
configuration file. See [search] section.
Show Docker container name #
If you have access permission to docker daemon ( unix:///var/run/docker.sock ), Docker column is added.
procs growi

Note that procs gets the container information through UNIX domain socket, so Docker Toolbox on macOS (doesn’t use UNIX domain socket) is not supported. Docker Desktop for Mac is supported but not tested.
Pager #
If output lines exceed terminal height, pager is used automatically. This behavior and pager command can be specified by configuration file.
Linux / macOS #
On Linux and macOS, less is the default pager.
If there is not less, more is used.
Instead of them, built-in pager can be used by configuration use_builtin.
Windows #
On Windows, built-in pager is always used.
Watch mode #
If --watch or --watch-interval <second> option is used, procs automatically updates output like top.
If --watch is used, the update interval becomes 1s.
The update interval can be specified by the argument of --watch-interval.
There are some keyboard shortcuts to control.
n: Change the sort column to the next columnp: Change the sort column to the previous columna: Change the sort order to ascendingd: Change the sort order to descendingq: Quit
Tree view #
If --tree option is used, processes are sorted by dependency order and dependency tree is shown at left side.
procs --tree

If TreeSlot column exists in config, dependency tree is shown at the slot.
Sort column #
Column sort order can be changed by --sorta or --sortd option.
The last character of --sorta and --sortd means sort order: “a"scending and “d"escending.
The column for sort is selected by the option keyword.
The keyword is matched with column kind that is shown by --list option.
If --sorta cputime, column is sorted by CpuTime with ascending order.
If --sortd rss, column is sorted by VmRss with descending order.
The keyword is matched partially and case is ignored.
The default sort is specified by [sort] section in the
configuration file.
procs --sortd cpu

Insert column #
--insert option inserts new column to the position of Slot column or MultiSlot column.
The column for insert is selected by the option keyword.
The keyword is the same as sort option.
A Slot column can be used by an inserted column.
If many insertions are required, many Slot columns should be added.
A MultiSlot column can be used by many inserted columns.
If there is a MultiSlot, all the remaining columns are inserted to the MultiSlot, and the subsequent Slot / MultiSlot is not used.
Unused Slot / MultiSlot is not shown.
Shell completion #
--gen-completion option generates shell completion files under the current directory.
The following shells are supported.
zshbashfishpowershellelvish
--gen-completion-out option generates shell completion to stdout.
You can source it directly on some shells.
source <(procs --gen-completion-out bash)
Configuration #
Configuration path #
You can change configuration by writing a configuration file.
There are some configuration examples in config directory of this repository.
config/large.toml is the default configuration before procs v0.9.21.
The location of the configuration file is OS-specific:
- Linux:
~/.config/procs/config.toml - macOS:
~/Library/Preferences/com.github.dalance.procs/config.toml - Windows:
~/AppData/Roaming/dalance/procs/config/config.toml
For compatibility, if ~/.procs.toml exists, it will be preferred to
the OS-specific locations.
Specify a configuration from command line #
--use-config option can specify a built-in configuration.
--load-config option can specify a configuration file path.
Configuration example #
The complete example of a configuration file can be generated by --gen-config option.
[[columns]]
kind = "Pid"
style = "BrightYellow|Yellow"
numeric_search = true
nonnumeric_search = false
[[columns]]
kind = "Username"
style = "BrightGreen|Green"
numeric_search = false
nonnumeric_search = true
align = "Right"
[style]
header = "BrightWhite|Black"
unit = "BrightWhite|Black"
tree = "BrightWhite|Black"
[style.by_percentage]
color_000 = "BrightBlue|Blue"
color_025 = "BrightGreen|Green"
color_050 = "BrightYellow|Yellow"
color_075 = "BrightRed|Red"
color_100 = "BrightRed|Red"
[style.by_state]
color_d = "BrightRed|Red"
color_r = "BrightGreen|Green"
color_s = "BrightBlue|Blue"
color_t = "BrightCyan|Cyan"
color_z = "BrightMagenta|Magenta"
color_x = "BrightMagenta|Magenta"
color_k = "BrightYellow|Yellow"
color_w = "BrightYellow|Yellow"
color_p = "BrightYellow|Yellow"
[style.by_unit]
color_k = "BrightBlue|Blue"
color_m = "BrightGreen|Green"
color_g = "BrightYellow|Yellow"
color_t = "BrightRed|Red"
color_p = "BrightRed|Red"
color_x = "BrightBlue|Blue"
[search]
numeric_search = "Exact"
nonnumeric_search = "Partial"
logic = "And"
[display]
show_self = false
show_thread = false
show_thread_in_tree = true
cut_to_terminal = true
cut_to_pager = false
cut_to_pipe = false
color_mode = "Auto"
[sort]
column = 0
order = "Ascending"
[docker]
path = "unix:///var/run/docker.sock"
[pager]
mode = "Auto"
[[columns]] section
#
[[columns]] section defines which columns are used.
The first [[columns]] is shown at left side, and the last is shown at right side.
| Key | Value | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| kind | See kind list |
Column type | |
| style | See style list |
Column style | |
| numeric_search | true, false | false | Whether the column can be matched with numeric keywords |
| nonnumeric_search | true, false | false | Whether the column can be matched with non-numeric keywords |
| align | Left, Right, Center | Left | Text alignment |
| max_width | [Number] | Maximum column width | |
| min_width | [Number] | Minimum column width | |
| header | [String] | Alternate header description |
kind list
#
procs kind |
ps STANDARD FORMAT |
Description | Linux | macOS | Windows |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Command | args | Command with all arguments | o | o | o |
| ContextSw | -not supported- | Context switch count | o | o | |
| CpuTime | cputime | Cumulative CPU time | o | o | o |
| Docker | -not supported- | Docker container name | o | o | |
| Eip | eip | Instruction pointer | o | ||
| ElapsedTime | -not supported- | Elapsed time | o | o | o |
| Env | e output modifier |
Environment variables | o | ||
| Esp | esp | Stack pointer | o | ||
| FileName | comm | File name | o | ||
| Gid | egid | Group ID | o | o | o |
| GidFs | fgid | File system group ID | o | ||
| GidReal | rgid | Real group ID | o | o | |
| GidSaved | sgid | Saved group ID | o | o | |
| Group | egroup | Group name | o | o | o |
| GroupFs | fgroup | File system group name | o | ||
| GroupReal | rgroup | Real group name | o | o | |
| GroupSaved | sgroup | Saved group name | o | o | |
| MajFlt | maj_flt | Major page fault count | o | o | o |
| MinFlt | min_flt | Minor page fault count | o | o | |
| MultiSlot | -not supported- | Slot for --insert option |
o | o | o |
| Nice | ni | Nice value | o | o | |
| Pgid | pgid | Process group ID | o | o | |
| Pid | pid | Process ID ( or Thread ID sorrunded by [] ) |
o | o | o |
| Policy | policy | Scheduling policy | o | o | |
| Ppid | ppid | Parent process ID | o | o | o |
| Priority | pri | Priority | o | o | o |
| Processor | psr | Currently assigned processor | o | ||
| ReadBytes | -not supported- | Read bytes from storage | o | o | o |
| RtPriority | rtprio | Real-time priority | o | ||
| SecContext | label | Security context | o | ||
| Separator | -not supported- | Show | for column separation |
o | o | o |
| Session | sid | Session ID | o | o | |
| ShdPnd | pending | Pending signal mask for process | o | ||
| SigBlk | blocked | Blocked signal mask | o | ||
| SigCgt | caught | Caught signal mask | o | ||
| SigIgn | ignored | Ignored signal mask | o | ||
| SigPnd | pending | Pending signal mask for thread | o | ||
| Slot | -not supported- | Slot for --insert option |
o | o | o |
| Ssb | -not supported- | Speculative store bypass status | o | ||
| StartTime | start_time | Starting time | o | o | o |
| State | s | Process state | o | o | |
| TcpPort | -not supported- | Bound TCP ports | o | o | |
| Threads | nlwp | Thread count | o | o | |
| TreeSlot | -not supported- | Slot for tree column | o | o | o |
| Tty | tty | Controlling TTY | o | o | |
| UdpPort | -not supported- | Bound UDP ports | o | o | |
| Uid | euid | User ID | o | o | o |
| UidFs | fuid | File system user ID | o | ||
| UidLogin | -not supported- | Login user ID | o | ||
| UidReal | ruid | Real user ID | o | o | |
| UidSaved | suid | Saved user ID | o | o | |
| UsageCpu | %cpu | CPU utilization | o | o | o |
| UsageMem | %mem | Memory utilization | o | o | o |
| User | euser | User name | o | o | o |
| UserFs | fuser | File system user name | o | ||
| UserLogin | -not supported- | Login user name | o | ||
| UserReal | ruser | Real user name | o | o | |
| UserSaved | suser | Saved user name | o | o | |
| VmData | -not supported- | Data size | o | ||
| VmExe | trs | Text segments size | o | ||
| VmHwm | -not supported- | Peak resident set size | o | o | |
| VmLib | -not supported- | Library code size | o | ||
| VmLock | -not supported- | Locked memory size | o | ||
| VmPeak | -not supported- | Peak virtual memory size | o | o | |
| VmPin | -not supported- | Pinned memory size | o | o | |
| VmPte | -not supported- | Page table entries size | o | ||
| VmRss | rss | Resident set size | o | o | o |
| VmSize | vsz | Physical page size | o | o | o |
| VmStack | -not supported- | Stack size | o | ||
| VmSwap | -not supported- | Swapped-out virtual memory size | o | o | |
| Wchan | wchan | Process sleeping kernel function | o | ||
| WorkDir | -not supported- | Current working directory | o | ||
| WriteByte | -not supported- | Write bytes to storage | o | o | o |
style list
#
- BrightBlack
- BrightRed
- BrightGreen
- BrightYellow
- BrightBlue
- BrightMagenta
- BrightCyan
- BrightWhite
- Black
- Red
- Green
- Yellow
- Blue
- Magenta
- Cyan
- White
- Color256
- ByPercentage
- ByState
- ByUnit
There are some special styles like ByPercentage, ByState, ByUnit.
These are the styles for value-aware coloring.
For example, if ByUnit is chosen, color can be specified for each unit of value ( like K, M, G,,, ).
The colors can be configured in [style.by_unit] section.
Other colors can be configured as the same as color.
[style] section
#
[style] section defines colors of header, unit and each styles.
The available list of color is below.
| Subsection | Key | Value | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| header | See color list |
BrightWhite|Black | Header color | |
| unit | See color list |
BrightWhite|Black | Unit color | |
| tree | See color list |
BrightWhite|Black | Tree color | |
| by_percentage | color_000 | See color list |
BrightBlue|Blue | Color at 0% - 25% |
| by_percentage | color_025 | See color list |
BrightGreen|Green | Color at 25% - 50% |
| by_percentage | color_050 | See color list |
BrightYellow|Yellow | Color at 50% - 75% |
| by_percentage | color_075 | See color list |
BrightRed|Red | Color at 75% - 100% |
| by_percentage | color_100 | See color list |
BrightRed|Red | Color at 100% - |
| by_state | color_d | See color list |
BrightRed|Red | Color at D state |
| by_state | color_r | See color list |
BrightGreen|Green | Color at R state |
| by_state | color_s | See color list |
BrightBlue|Blue | Color at S state |
| by_state | color_t | See color list |
BrightCyan|Cyan | Color at T state |
| by_state | color_z | See color list |
BrightMagenta|Magenta | Color at Z state |
| by_state | color_x | See color list |
BrightMagenta|Magenta | Color at X state |
| by_state | color_k | See color list |
BrightYellow|Yellow | Color at K state |
| by_state | color_w | See color list |
BrightYellow|Yellow | Color at W state |
| by_state | color_p | See color list |
BrightYellow|Yellow | Color at P state |
| by_unit | color_k | See color list |
BrightBlue|Blue | Color at unit K |
| by_unit | color_m | See color list |
BrightGreen|Green | Color at unit M |
| by_unit | color_g | See color list |
BrightYellow|Yellow | Color at unit G |
| by_unit | color_t | See color list |
BrightRed|Red | Color at unit T |
| by_unit | color_p | See color list |
BrightRed|Red | Color at unit P |
| by_unit | color_x | See color list |
BrightBlue|Blue | Color at other unit |
color list
#
- BrightBlack
- BrightRed
- BrightGreen
- BrightYellow
- BrightBlue
- BrightMagenta
- BrightCyan
- BrightWhite
- Black
- Red
- Green
- Yellow
- Blue
- Magenta
- Cyan
- White
- Color256
Colors can be configured by theme through |.
style = "BrightWhite|Black" # BrightWhite for dark theme and Black for light theme
style = "BrightWhite" # BrightWhite for both theme
The first color is for dark theme, and the second is for light theme. If only a color is specified, the color is applied to both theme.
Color256 can be specified by 0-255 value like below:
style = "223|112" # 223 for dark theme and 112 for light theme
style = "223" # 223 for both theme
[search] section
#
[search] section defines option for Keyword search.
| Key | Value | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| numeric_search | Exact, Partial | Exact | Whether numeric keywords match exactly or partially |
| nonnumeric_search | Exact, Partial | Partial | Whether non-numeric keywords match exactly or partially |
| logic | And, Or, Nand, Nor | And | Logical operation between keywords |
| case | Smart, Insensitive, Sensitive | Smart | Case sensitivity in search |
case
#
case is case sensitivity in search.
Smart: If keyword contains uppercase character, case sensitive search. Otherwise case insensitive searchInsensitive: case insensitive searchSensitive: case sensitive search
[display] section
#
[display] section defines option for output display.
| Key | Value | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| show_self | true, false | false | Whether the self process ( procs ) is shown |
| show_thread | true, false | false | Whether the thread information is shown ( Linux only ) |
| show_thread_in_tree | true, false | true | Whether the thread information is shown in tree mode ( Linux only ) |
| show_parent_in_tree | true, false | true | Whether the parent process is shown in tree mode |
| show_children_in_tree | true, false | true | Whether the children processes are shown in tree mode |
| show_header | true, false | true | Whether header row is shown |
| show_footer | true, false | false | Whether footer row is shown |
| cut_to_terminal | true, false | true | Whether output lines are truncated for output into terminal |
| cut_to_pager | true, false | false | Whether output lines are truncated for output into pager |
| cut_to_pipe | true, false | false | Whether output lines are truncated for output into pipe |
| color_mode | Auto, Always, Disable | Auto | The default behavior of output coloring without --color commandline option |
| separator | [String] | │ | String used as Separator |
| ascending | [String] | ▲ | Ascending sort indicator |
| descending | [String] | ▼ | Descending sort indicator |
| tree_symbols | [String; 5] | [│, ─, ┬, ├, └] | Symbols used by tree view |
| abbr_sid | true, false | true | Whether machine SID is abbreviated ( Windows only ) |
| theme | Auto, Dark, Light | Auto | Default theme |
If color_mode is Auto, color is enabled for terminal and pager, disabled for pipe.
If theme is Auto, theme is detected from terminal automatically.
Some terminal don’t support the automatic detection, so Dark or Light can be specified explicitly.
abbr_sid
#
Windows SID is too long, so it is abbreviated by default.
If abbr_sid is false, SID is fully shown like below:
S-1-5-21-789457439-2186958450-1652286173-1001
If abbr_sid is true, SID is shown like below:
S-1-5-21-...-1001
[sort] section
#
[sort] section defines the column used for sort and sort order.
| Key | Value | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| column | [Number] | 0 | Column number to used for sort |
| order | Ascending, Descending | Ascending | Sort order |
If column is 0, value is sorted by the left column.
[docker] section
#
[docker] section defines how to communicate to docker daemon.
| Key | Value | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| path | [Path] | unix:///var/run/docker.sock | UNIX domain socket to docker daemon |
[pager] section
#
[pager] section defines the behavior of pager.
| Key | Value | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| mode | Auto, Always, Disable | Auto | The default behavior of pager usage without --pager commandline option |
| detect_width | true, false | false | Whether auto mode detects terminal width overflow |
| use_builtin | true, false | false | Whether built-in pager is used |
| command | [Command] | less -SR | Pager command |
If mode is Auto, pager is used only when output lines exceed terminal height.
Default pager is less -SR ( if less is not found, more -f ).